The growing trend of solar power for home use highlights significant benefits for homeowners. In 2022, the Solar Energy Industries Association reported a 20% increase in residential solar installations. This trend illustrates a shift toward renewable energy sources and decreasing reliance on fossil fuels. Experts point out the cost-effectiveness of solar panels, which can lead to substantial savings on electricity bills.
John Smith, a leading solar energy analyst, emphasizes, "Investing in solar power for home is not just an environmental choice; it's a financial one." This perspective reflects the increasing affordability of solar technologies. Many homeowners, however, still hesitate. They often question the initial costs and long-term investments.
There are various options available in solar technology, from rooftop panels to solar shingles. Each choice has its merits and limitations, giving potential users plenty to consider. As the industry evolves, homeowners must stay informed and reflect on their options. Adopting solar can feel overwhelming, but with the right resources, the transition can become manageable.

Solar power for residential use has gained significant traction in recent years. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, solar energy accounted for about 3.1% of total electricity generation in 2020. This number is projected to rise as more homeowners explore solar options. Many households are looking to reduce energy costs while contributing to environmental sustainability.
The benefits are substantial. Homeowners can save over $20,000 on energy bills throughout the system's lifetime. A typical solar panel installation can reduce carbon emissions by nearly 100,000 pounds over 30 years. However, it’s essential to consider the initial costs and installation challenges. Some homeowners find the upfront investment daunting. Financial incentives and tax credits can help ease this burden, but they vary by location.
Despite the advantages, some drawbacks exist. Not all homes are suitable for solar panels due to roof orientation or shading issues. Furthermore, the effectiveness of solar systems can fluctuate with weather changes. For many, the decision to switch to solar requires thorough research and planning. It’s not just about the technology; it’s about understanding personal needs and long-term goals.
| Benefit/Option | Description | Potential Savings | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Energy Bills | Solar panels generate electricity, which can drastically reduce your monthly utility bills. | Up to 70% reduction | Reduces reliance on fossil fuels |
| Increased Home Value | Homes with solar power systems can sell for more than those without. | Average increase of $15,000 | Encourages use of renewable energy |
| Government Incentives | Tax credits and rebates are available to offset initial installation costs. | Up to 26% federal tax credit | Promotes clean energy initiatives |
| Energy Independence | Generating your own power reduces dependence on external sources. | N/A | Decreases carbon footprint |
| Low Maintenance Costs | Solar panels require minimal maintenance, mainly regular cleaning. | Generally low upkeep costs | Enhances sustainability |
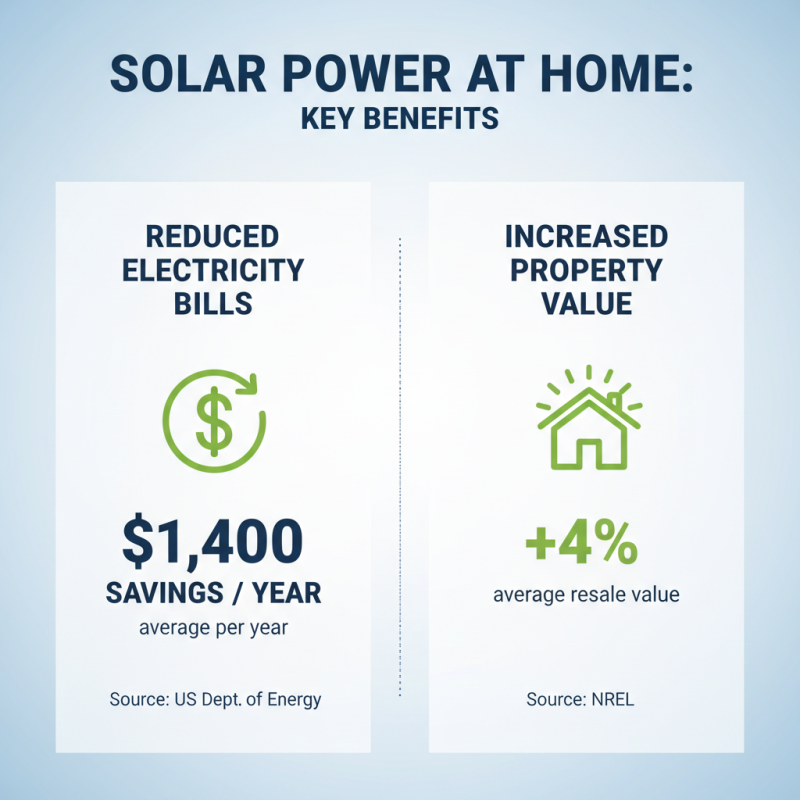
Installing solar power at home offers significant benefits that homeowners should consider. One key advantage is the reduction in electricity bills. A study from the U.S. Department of Energy shows that homeowners can save an average of $1,400 annually by using solar energy. This saving can help offset installation costs over time. Additionally, solar power increases property value. Properties with solar panels can sell for an average of 4% more than those without, according to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory.
Environmental impact is another important benefit. Solar energy is clean and renewable. It reduces reliance on fossil fuels, which are harmful to the planet. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency states that solar power systems can reduce greenhouse gas emissions significantly. However, some may not have the ideal roof space or sunlight exposure for efficient solar installation. This limitation can raise questions about solar feasibility for certain homes.
Lastly, various financing options and incentives are available. Many states and local governments offer tax credits and rebates for solar installation. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association, nearly 90% of homes are eligible for some form of incentive. Yet, navigating these options can be complex. Homeowners must do thorough research to maximize their benefits.
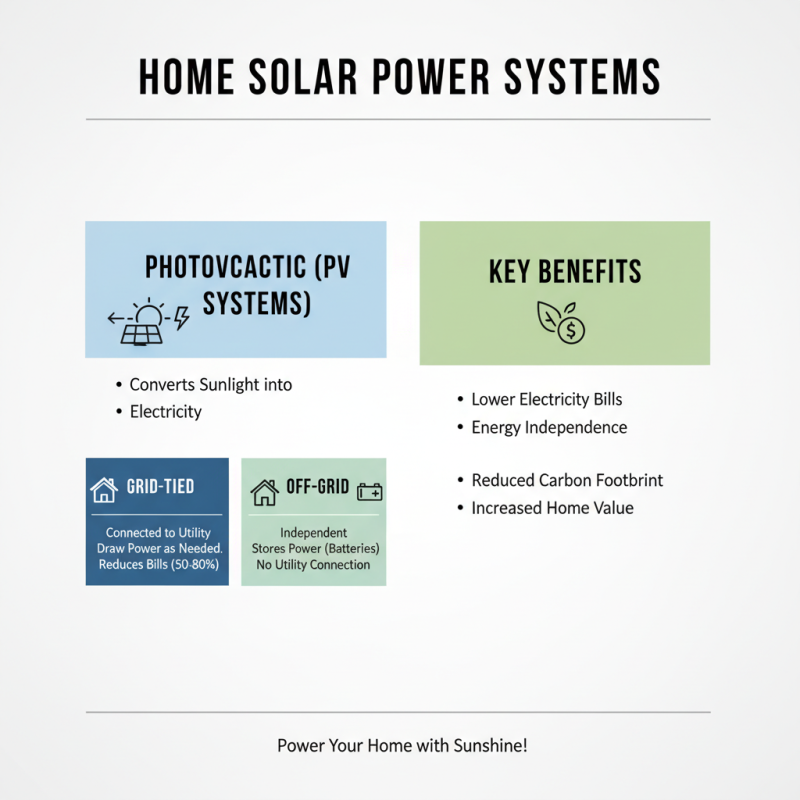
When considering solar power systems for homeowners, it's important to understand the different types available. Photovoltaic (PV) systems convert sunlight into electricity. These can be either grid-tied or off-grid. A grid-tied system connects to the local utility. It allows homeowners to draw power when needed. This system can reduce electricity bills significantly. Studies show these systems can lower electricity costs by 50-80%.
Another option is solar thermal systems. They use sunlight to heat water for domestic use. This is an excellent choice for those needing hot water year-round. A report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) indicates that solar thermal systems can increase energy efficiency by up to 30%. However, they require adequate space for installation, which some homeowners may lack.
Hybrid systems combine PV and solar thermal technologies. They offer flexibility but can be complex. Homeowners must consider their specific energy needs. Moreover, installation costs can be a barrier. A survey indicated that while 70% of homeowners are interested in solar, only 15% follow through due to perceived complications. Evaluating all options carefully is essential for making a well-informed choice.
Choosing solar power for your home is a significant decision. Several factors affect your options. One key aspect is your location. Sunlight intensity varies greatly. Homes in sunny areas often benefit more. Data reveals that solar capacity can reach 300% more in ideal climates.
Your roof type also plays a crucial role. If you have a flat roof, installation can be straightforward. However, a sloped roof may need more equipment. The orientation of your roof affects efficiency. South-facing roofs typically capture more sunlight.
Cost is another major consideration. While initial investment is high, reports show savings can exceed 50% on energy bills over time. However, financing options can complicate choices. It's essential to evaluate your budget and long-term plans.
Tip: Research local incentives. Many regions offer rebates or tax credits. This can significantly lower your overall costs.
Remember, not every home will maximize solar benefits. Some homes face shading issues. Others may lack sufficient roof space. Understanding your specific situation is vital. Take your time and assess all factors carefully.
This chart illustrates the various benefits of solar power for homes, emphasizing cost savings, positive environmental impact, and other significant advantages. The percentages reflect the importance homeowners place on each benefit when considering solar power options.
When considering solar power for home systems, understanding costs is essential. The initial installation can seem daunting. Average prices for solar panels vary widely depending on location, system size, and installation type. Homeowners might spend anywhere from $15,000 to over $25,000. However, this figure often doesn't include available incentives.
Government programs can significantly reduce overall costs. Tax credits and rebates help ease the financial burden. For instance, many regions offer incentives that can cover up to 30% of installation costs. Still, navigating these options requires research. Not all benefits apply everywhere. Some homeowners might feel overwhelmed by the choices.
Financing options exist for those who can't afford upfront costs. Loans, leases, and power purchase agreements are popular. Each option has its pros and cons. A loan might seem favorable, but it increases long-term debt. Leases can be simpler but may not build equity in your home. It's crucial to evaluate what's best for your situation. This requires careful thought and sometimes professional advice.