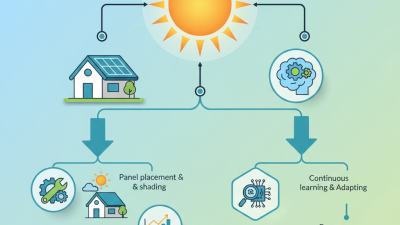
As we face escalating environmental challenges, solar installation emerges as a vital solution for a sustainable future. Renowned solar energy expert Dr. Lisa Greene once stated, "Solar energy is not just a resource, it’s our lifeline for tomorrow." This perspective highlights the urgency of transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar power. The increasing demand for cleaner energy requires immediate action to reduce our carbon footprint.
Investing in solar installation significantly lowers greenhouse gas emissions. In many regions, solar panels can generate electricity efficiently, saving money on utility bills. However, despite these benefits, some hold reservations about the initial costs of installation. This hesitation often stems from a lack of understanding about long-term savings and available incentives. Transparent communication is essential to counter this skepticism.
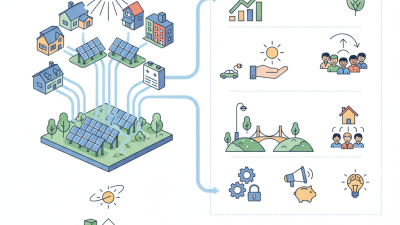
Moreover, solar installation can empower communities. It creates jobs and stimulates local economies. Yet, disparities remain in access to solar technology across different socioeconomic groups. Addressing these gaps is critical for an equitable energy transition. Therefore, fostering awareness and investing in solar infrastructure must be prioritized to pave the way for a sustainable energy landscape.

The impact of solar energy on climate change is profound. Solar power is a clean alternative to fossil fuels. It reduces greenhouse gas emissions significantly. By harnessing sunlight, we can lessen our reliance on pollution-heavy energy sources. The technology is simple: solar panels convert sunlight into electricity. This process emits no harmful substances. However, installation can be costly and complex for many households.
Transitioning to solar energy isn't without challenges. Some regions have limited sunlight, affecting efficiency. Also, environmental concerns arise from manufacturing solar panels.
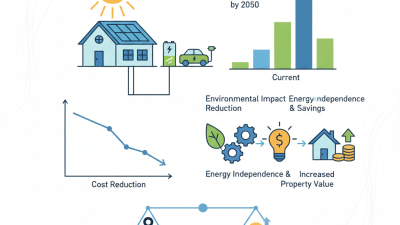
Yet, if managed properly, the benefits outweigh the drawbacks. Every solar panel installed is a step towards a cleaner planet. Communities can lower their carbon footprints. The shift to solar energy encourages innovation and jobs in green technology.
We still have a long way to go. More awareness is needed to educate the public. Many still underestimate solar energy's potential. Collaboration among governments, businesses, and individuals can drive change. Embracing solar energy is essential. It is not just an option; it is a necessity for future generations.
Solar installation significantly boosts local economies. Communities that invest in solar energy create new jobs. These jobs range from installation to maintenance. Many workers benefit from training programs. This leads to skill development, which enhances career prospects.
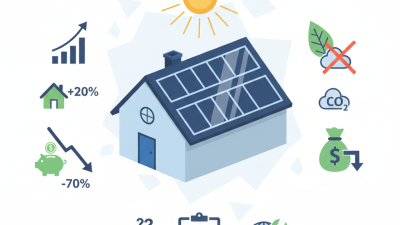
Additionally, solar energy reduces electricity costs. Households using solar power save money in the long run. This affordability helps families allocate more to other needs. Businesses also experience reduced energy bills, allowing for reinvestment in growth. Solar power can even increase property values.
However, challenges remain. Some communities face initial installation costs. Financing options might not be accessible for everyone. This can delay the transition to renewable energy. Greater awareness and support are needed to ensure everyone benefits from solar installations. Taking steps toward accessibility is crucial for a sustainable future.
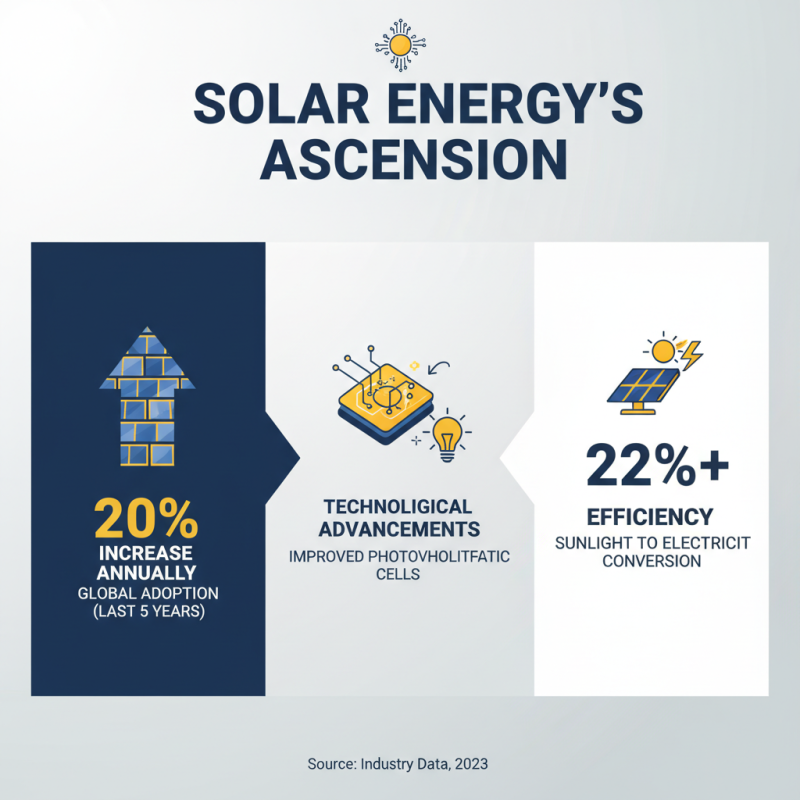
The rise of solar energy is closely tied to technological advancements. Recent data shows that solar adoption has increased by over 20% annually in the past five years. Innovations in photovoltaic cells have greatly improved efficiency. Now, some panels convert more than 22% of sunlight into electricity. This efficiency is crucial as it enhances energy output.
Battery technology is also evolving. Energy storage solutions are becoming more affordable. A report by the International Energy Agency highlights that battery costs have dropped by 89% since 2010. This decline allows homeowners to store solar energy for later use. The combination of improved solar panels and advanced batteries is driving widespread adoption.
However, challenges remain. Not all regions benefit equally from solar energy. Weather patterns can limit effectiveness in some areas. Additionally, installation costs may still deter some homeowners. Despite these obstacles, the overall trend shows a positive shift towards a more sustainable energy future. The potential is vast, but the journey requires continuous exploration and reflection.
Government policies play a crucial role in promoting solar energy initiatives. They create a framework that encourages investments and innovation. Many countries offer tax incentives and rebates for solar installation. For instance, a recent report shows that these incentives can reduce installation costs by up to 30%. This significant reduction makes solar energy more accessible.
However, some policies fall short. They might lack sufficient funding or comprehensive support. In the U.S., for example, the solar industry has faced challenges due to inconsistent state-level policies. According to the Solar Energy Industries Association (SEIA), this inconsistency can lead to a decrease in new installations by over 50% in some regions. It’s crucial for governments to review their strategies and ensure they provide robust support for solar initiatives.
Moreover, the need for improved infrastructure remains evident. Many areas still lack the grid capabilities to handle increased solar energy. A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) highlights that 50% of the U.S. grids require upgrades to utilize solar power effectively. Addressing these issues is vital for realizing the full potential of solar energy.
The following chart illustrates the adoption of solar energy in various countries, highlighting the installed solar power capacity (in GW) as a measure of sustainability efforts backed by government policies.
Solar energy plays a vital role in achieving energy independence. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, solar power could generate up to 40% of the nation’s electricity by 2035. This shift reduces reliance on imported fossil fuels. It also enhances national security by diversifying energy sources.
Communities adopting solar installations witness transformative effects. Local economies improve as jobs in installation and maintenance grow. A 2020 report from the Solar Foundation indicated that the solar industry employed over 250,000 workers in the U.S. This job growth can be critical for areas with limited job opportunities.
Tip: Consider community solar projects. They allow multiple households to access solar energy without individual installations.
However, not every area has optimal solar conditions. Some regions experience less sunlight. Roof space limitations also present a challenge. This means solar installations are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Awareness of local conditions is essential.
Tip: Research available incentives before installation. Many states offer tax credits or rebates for solar projects. This can significantly reduce initial costs.
| Dimension | Data |
|---|---|
| Current Global Solar Capacity (GW) | 1,000 |
| Projected Growth Rate (2023-2030) | 20% CAGR |
| Reduction in CO2 Emissions per kWh | 0.4 kg |
| Average Solar Panel Lifespan (years) | 25 |
| Percentage of Energy Independence Achieved | 30% |
| Job Creation in Solar Sector (2023) | 250,000 |
| Average Savings on Electricity Bills (Annual) | $1,200 |